How to create a fully crud API in less than 5 minutes In Laravel!
How to create a fully crud API in less than 5 minutes with the unit test by writing In Laravel
Good day, today we are going to build a fully CRUD system (Web & API). API is a software intermediary that allows two applications to talk to each other. Somethings you might need to create an app that can be run on different languages or frameworks, for example, you can use Laravel to create the backend for your application while the frontend might run on any JavaScript frameworks. API allows two or more programs to communicate with each other. There are different types of APIs, but today we are going to concentrate on RESTful APIs. REST stands for Representational State Transfer, while API stands for Application Programming Interface. You can read more about API from the internet or other programming material.
Click on my profile to follow me to get more updates.
Prerequisites
We'll use a laravel package called Laragine, this package helps us to create a fully CRUD system by just writing simple commands Without saying much, let's dive into it.
What is Laragine?
Laragine is a laravel package which was created to manage your large laravel app using modules, let's say that you'll build a blog the blog consist of (post - comment - like), blog-> is a module, (post - comment - like) -> called units laragine built the module & units with all CRUD functionalities also built (Migrations - factories - tests - controllers - models) all you have to do is to just include the link in route files, awesome, right!
In this tutorial, we'll just create a post for a blog with fully CRUD functionalities so we'll create a module called blog then we'll create a unit called post
STEP 1: install laravel 8
To install the latest laravel framework, which is laravel 8.0 as of the time of publishing this article, run the command below
composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel laravel_8
This will automatically create a laravel 8 app and some couple of things have been set up, we don’t need to copy and rename the env.example file, Laravel 8 does that automatically for us.

Another important thing about Laravel 8, you don’t need to generate APP_KEY, this new version will also generate it for us.

With that all set up, our app is ready.
STEP 2: Database setup
Create an empty database, Open the .env file, and update your database configurations.

STEP 3: Require Laragine package
Let us install Laragine.
composer require yepwoo/laragine

STEP 4: Install the package
After including Laragine, you have to install it by running the following command:
php artisan laragine:install
it's an initial command for Laragine

Note
After running the command, the Laragine directory will be in the root directory under core directory.

If you want to know more information about the package visit the documentation
STEP 5: Create a blog module
Run the following command and specify the name of the module in our case will be blog
php artisan laragin:module blog
Any module will be added under
core directory After running the command, the blog directory will be in thecore` directory.
STEP 6: Create unit
After creating our module (blog) we need to create a post, right?
The unit command consists of 2 commands
Init command:
Creates all basic files and will create a JSON file that we'll specify the attributes that we want to add it to the database, we should specify the name of the module that we want to add the unit under it, which is blog in this example.
Second command:
it's the same command without init option, the command will automatically create all the following files depending on the data that we specified in the JSON file.
- Migration
- Requests
- Resources
- Factories
- unit tests
let's run the commands, we should specify name of the module that we want to create the unit under it & the name of unit
php artisan laragin:unit post --module=blog --init
We include --init because it's the first part of unit command
After running the command it'll generate the basic files Controller (API - web) - Model & also the JSON file that we'll write our attributes in it.

- Now we should specify our attributes in the
Post.jsonfile, let's first know what the attributes that we need! let's start with the basics in this article I just want to show you how to use the package, you can add any amount of attributes you want, any post havetitle, body, thumbnail
Note
if we don't put the attribute as nullable will be required by default
Attributes:
- title -> type:
string, definition:unique - body -> type:
text, - image -> type:
string, definition:nullable
Now let's go to the JSON file which is in core/blog/data/Post.json to write our attributes.
Note
we should follow rules when writing any attribute in JSON file, there are two types of configuration type & definition
type:is the type of attribute you should write it asLaravelspecified in docs you can check all types in Laravel from heredefinition:is for column modifier also you should write it as `Laravel specified in the docs you can check it from here
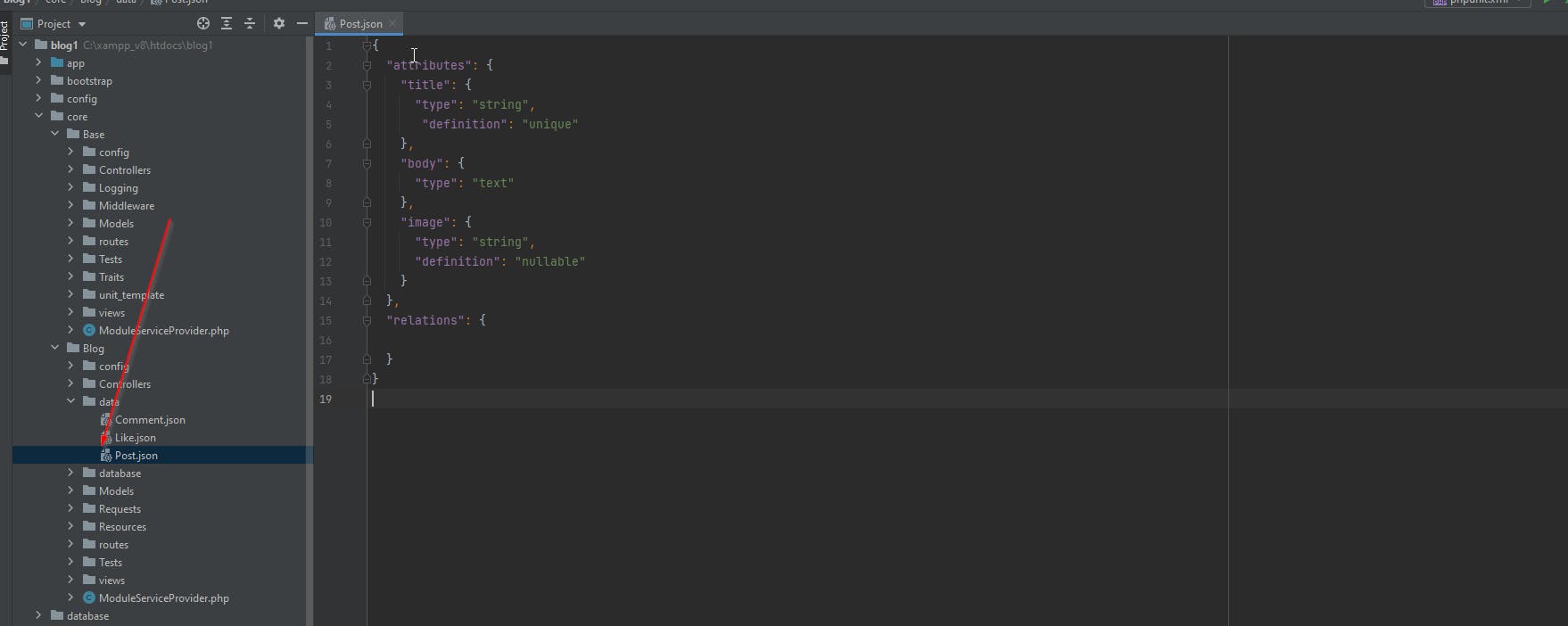
if you realized that I didn't write required because the package will add it automatically.
Let's run the second part of unit command
php artisan laragin:unit post --module=blog
After running the command it'll generate migrations - requests - resources - factories - unit tests - etc... files and they are fully implemented.
let's see the migration file, you'll see all attributes are added automatically with the configuration that we specified in JSON file, magic, right🧐!
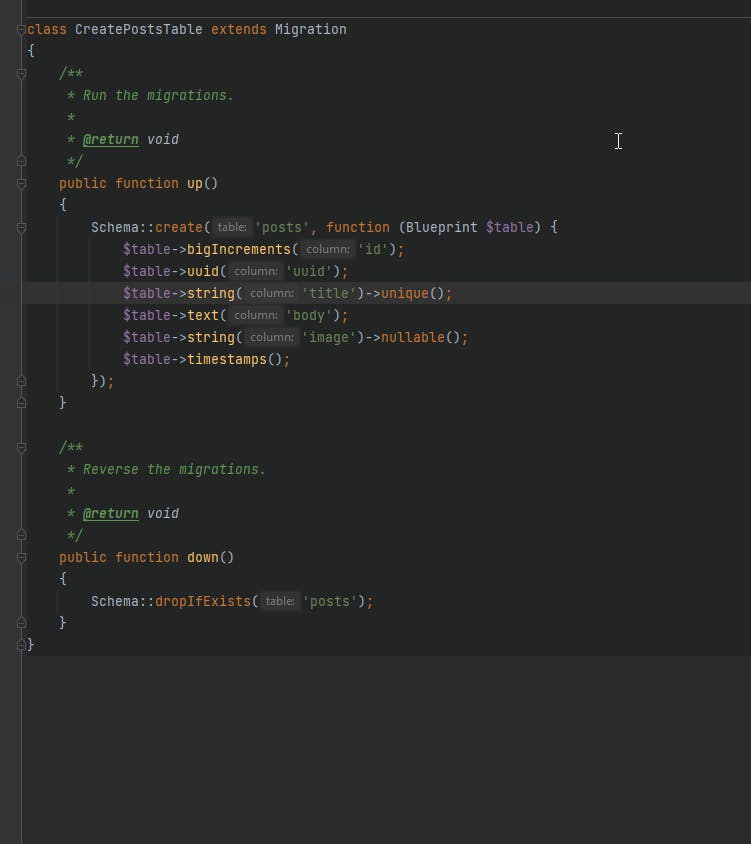
- Now let's run
migrate commandphp artisan migrate
STEP 7: Add API route
add Route::apiResource('posts', 'PostController'); in api.php in core\Blog\routes\api.php

Note
- we don't need to implement
CRUDmethods, it's aleardy implemented inPostControllerincore\Blog\Controllers\API\PostController.
STEP 8: Testing
- open
Postmanor any other software you use to test theAPI let's first create a new post

let's create another post but without including the
titleto just test if it'll returnerroror not
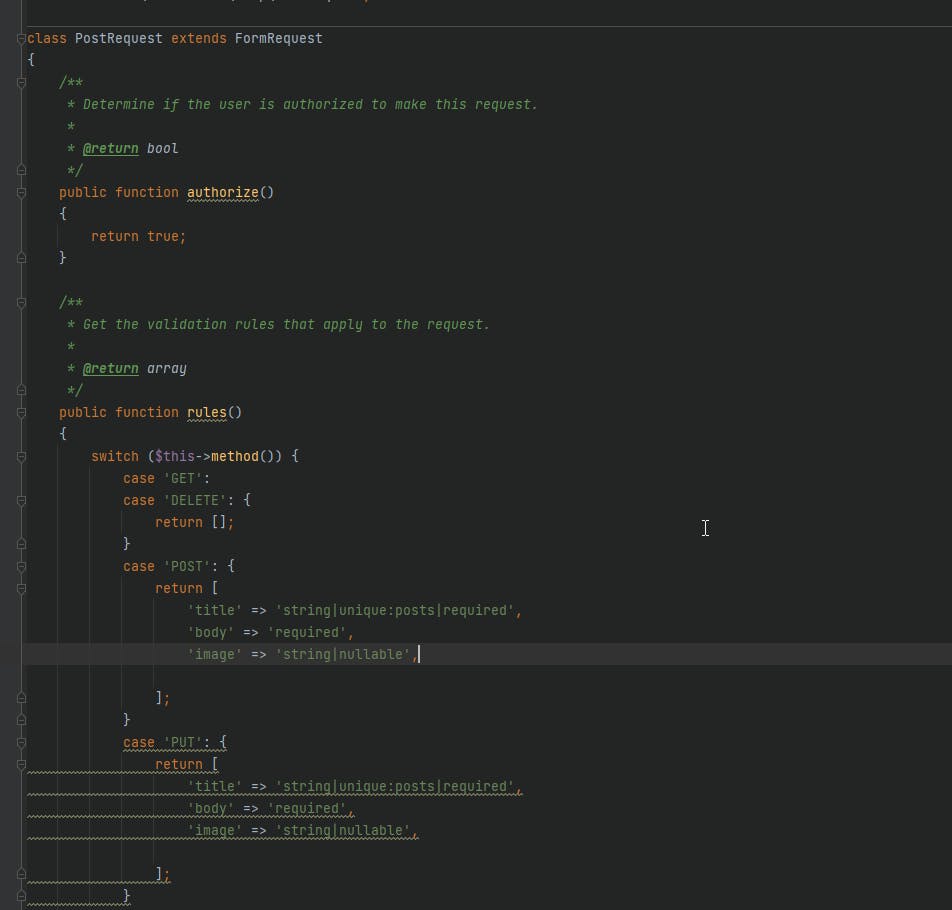
Now you're wondering how it gives us that the
titleattribute is required, right 🤔? let's seePostRequestfile incore/Blog/Requests, all attributes that we specefied is in the file with somevalidation,Laraginedoes this job for us.
note
you can modify any attribute you want in request file or in any other file Resources - unit test - etc...
Let's
getallposts
Let's
updatethe post before testing update method, you may want to change thevalidationin the update request (put) and you can do this fromPostRequestincore/Blog/Requestsfile inputmethod

- Let's
deletethe post
Conclusion
in this article I just showed you one feature of Laragine package, in the next tutorial I'll teach you how to use
unit tests by just making a small configuration.
Let's connect on LinkedIn

